There are no products listed under this category.
Welcome to CM Online Store!
Antibody Drug Conjugate Kits!
AqT bioconjugates coming soon!
Biotin, also known as vitamin H, is a coenzyme involved in the metabolism of fatty acids, leucine, and glucose. It binds noncovalently to streptavidin and avidin with exceptionally high affinity and specificity. In fact, the avidin–biotin interaction is the strongest known noncovalent protein–ligand interaction (Ka ≈ 10¹⁵ M⁻¹). This powerful binding has been widely applied in biotechnology for protein purification, detection, and assay development.
The process of attaching biotin or a biotin analog to a biomolecule is called biotinylation. Because biotin is highly hydrophobic, it must be dissolved in an organic solvent before being used in bioconjugation reactions carried out in aqueous buffers. Excessive biotinylation of biomolecules—particularly proteins—can lead to aggregation, so controlling the degree of labeling is critical. Various strategies are available to achieve controlled biotinylation. Typically, the carboxyl group of biotin is derivatized to create functional derivatives suitable for conjugation without affecting its binding properties.
Example 1: Biotinylation of protein at CellMosaic (only 52% pure starting protein was used and over 99.9% pure of biotinylated protein was isolated.)
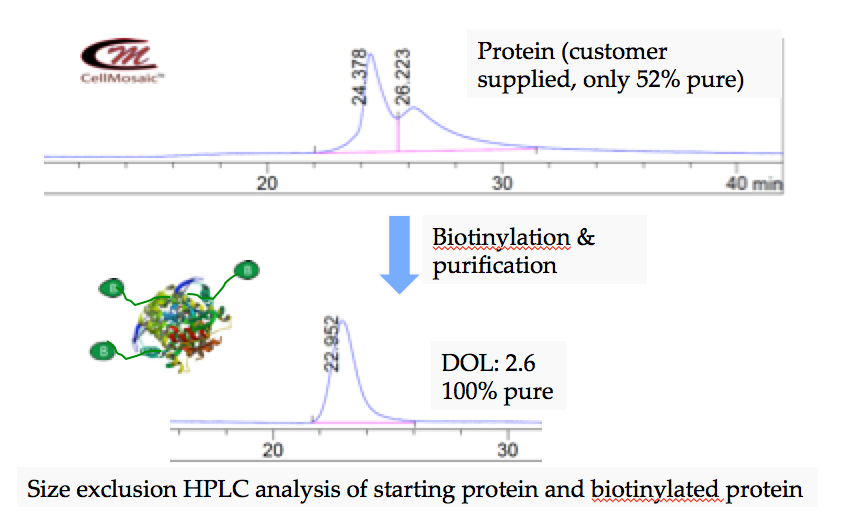
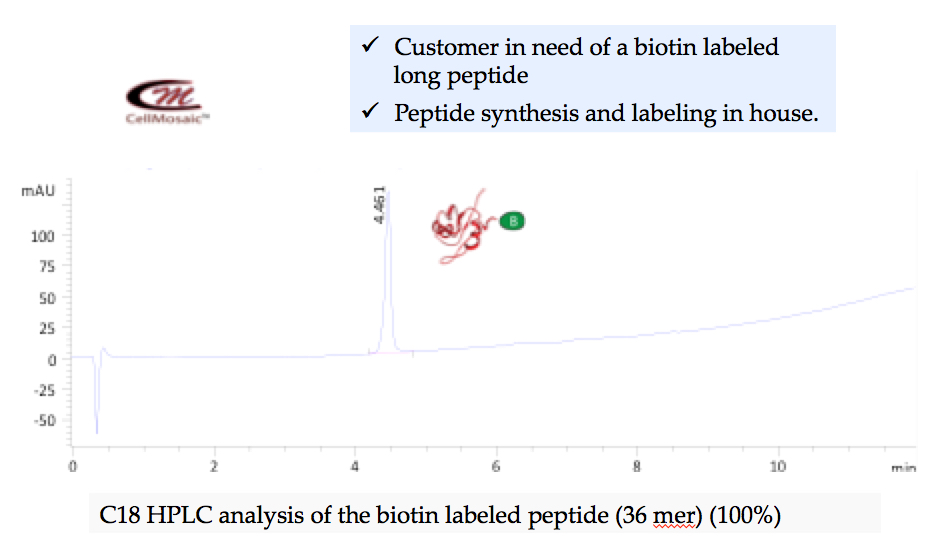
Example 2: Clean synthesis of a biotinylated peptide on solid phase at CellMosaic.
There are no products listed under this category.