Surface Activation
This is an intermediate step that prepares functionalized solid support for biopolymer immobilization. Some of the solid supports are available commercially in active form . For non-active solid supports, we can either convert them to an activate form first or let them react directly to a biopolymer using active coupling reagents.
CellMosaic uses these processes exclusively for supporting our custom Biopolymer Immobilization.
Example 1: CNBr activation of agarose.
- Description
- Scheme
- References
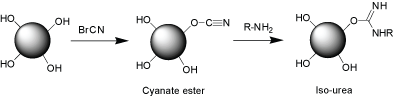
The preparation of active esters of hydroxyl-containing solid supports for reaction with amine-containing biopolymers or small molecules.
- Chemistry: Cyanogen bromide reacts with hydroxyl groups to form a cyanate ester.
- Starting materials: Solid supports containing hydroxyl groups such as agarose.
- Note: CNBr-activate solid supports produced in CellMosaic will be used directly for the large scale immobilization of antigens/antibodies due to the stability issue of active cyanate esters.
Activation of solid supports by BrCN
1. Axén, R.; Porath, J.; Ernback, S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967, Jun 24;214(5095):1302-4.
2. Porath, J.; Aspberg, K.; Drevin, H.; Axén, R. Preparation of cyanogen bromide-activated agarose gels. J Chromatogr. 1973, 86, 53-65.
3. March, S. C.; Parikh, I; Guatrecasas, P. A. Simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Analytical Biochem. 1974, 60, 149-152.
4. Kohn, J.; Wilchek, M. A colorimetric method for monitoring activation of sepharose by cyanogen bromide. Biochem Biophys Research Communications 1978, 84, 7-14.
